[A Matlab script for the following example is avalable at examples/case_tomography/sippi_AM13_metropolis_gaussian_covariance_inference.m.]
One of the most intriguing benefits (in addition to the computational efficiency) of using the FFTMA type a priori model, is that it allows separation of the random component and the covariance model parameters. See [HCLM13a].
This means that one can in SIPPI define an inverse problem, where the a priori model is Gaussian, but where the properties of the Gaussian model (such as the mean, range, anisotropy) can be treated as unknown model parameters
Each property the Gaussian prior model that should be treated as an unknown model parameter, must be defined as a separate 1D type GAUSSIAN type prior model, with a specific name (identifying the covariance model property it describes), and it mist point to the prior model type number for which it describes a covariance model property-
The example below describes a 2D FFTMA type e a priori model (prior with id 1) with an unknown range (prior with id 2) with an a priori distribution described by a close to uniform distribution between 1.5m and 10.5m:
im=1;
prior{im}.type='FFTMA';
prior{im}.name='Velocity (m/ns)';
prior{im}.m0=0.145;
prior{im}.Va='.0003 Sph(6)';
dx=0.25;
prior{im}.x=[-1:dx:6];
prior{im}.y=[0:dx:13];
prior{im}.cax=[.1 .18];
i_master=im;
% range - horizontal
im=im+1;
prior{im}.type='gaussian';
prior{im}.name='range_1'; % the name covariance model property to define
prior{im}.m0=6;
prior{im}.min=1.5;
prior{im}.max=10.5;
prior{im}.norm=50;
prior{im}.prior_master=i_master; % point to the id of the prior it describes
Any combination of the following parameters can be set:
prior{im}.name='range_1; % Range, along direction of angle_1
prior{im}.name='range_2; % Range, along direction of angle_2
prior{im}.name='range_3; % Range, along direction of angle_3
prior{im}.name='ang_1; % Angle 1, degrees from North
prior{im}.name='ang_2; % Angle 2
prior{im}.name='ang_3; % Angle 3
prior{im}.name='sill; % sill,
prior{im}.name='nu; % the 'nu' parameter, only applies when using the Matern covariance model type.
prior{im}.name='m0; % A priori mean
As an example consider case where the two ranges, and the angle of anisotropy fro a 2D Gaussian(FFTMA) a priori type model is treated as model parameters:
im=0;
% velocity field
im=im+1;
prior{im}.type='FFTMA';
prior{im}.name='Velocity (m/ns)';
prior{im}.m0=0.145;
prior{im}.Va='.0003 Sph(6)';
dx=0.25;
prior{im}.x=[-1:dx:6];
prior{im}.y=[0:dx:13];
prior{im}.cax=[.1 .18];
i_master=im;
% range - horizontal
im=im+1;
prior{im}.type='gaussian';
prior{im}.name='range_1';
prior{im}.min=1.5;
prior{im}.max=10.5;
prior{im}.norm=50;
prior{im}.prior_master=i_master;
% range - horizontal
im=im+1;
prior{im}.type='gaussian';
prior{im}.name='range_2';
prior{im}.min=1.5;
prior{im}.max=5.5;
prior{im}.norm=50;
prior{im}.prior_master=i_master;
% rotation
im=im+1;
prior{im}.type='gaussian';
prior{im}.name='ang_1';
prior{im}.m0=90;
prior{im}.std=20;
prior{im}.norm=2;
prior{im}.prior_master=i_master;
A sample from the corresponding a priori model (FFTMA type) is shown below:
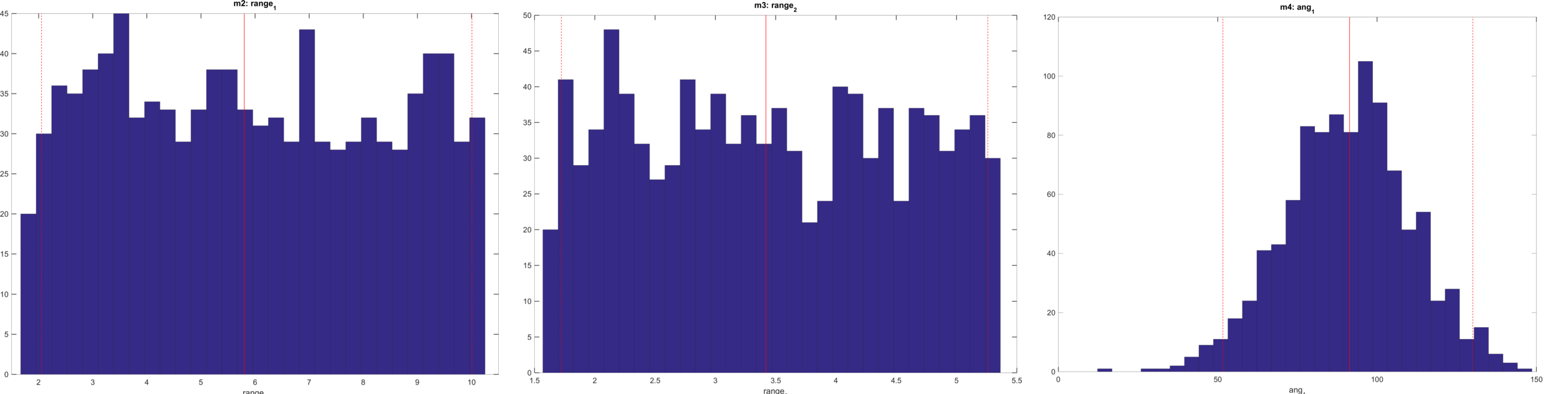
Samples of the a priori distributions for range_1, range_2, and ang_1 are shown here:
Figure 4.8. Distribution of one sample of a 1D Gaussian distribution describing range_1, range_2, and ang_1
 |
As for the examples above, the a posteriori distribution can be samples using e.g.
options.mcmc.nite=500000; % optional, default:nite=30000 options.mcmc.i_sample=500; % optional, default:i_sample=500; options.mcmc.i_plot=1000; % optional, default:i_plot=50; options=sippi_metropolis(data,prior,forward,options); % plot posterior statistics sippi_plot_posterior(options.txt);
